Last Updated: August 25, 2025

Technical SEO forms the foundation of a high-performing website. It ensures that your website is optimized for search engines and provides an exceptional user experience. This detailed guide will walk you through all critical aspects of technical SEO, step by step, to help you excel in 2025.
What is technical SEO?
Technical SEO is the process of optimizing your website for crawling, indexing, and ranking on search engines. Unlike on-page SEO (content optimization) and off-page SEO (link-building strategies), technical SEO focuses on the backend of your website.
Importance of technical SEO
Technical SEO is the backbone of a successful online presence, ensuring that a website is search engine-friendly and capable of delivering a seamless user experience. Here’s why Technical SEO is essential:
1. Improves crawlability & indexing
- Search engines can find your content: Technical SEO ensures that search engine crawlers can effectively navigate and index your site. Proper use of sitemaps, robots.txt files, and structured data helps search engines understand your site’s structure and prioritize its content.
- Avoids missing pages: Pages that aren’t crawled won’t appear in search results, impacting visibility.
2. Enhances website speed & performance

- Better user experience: Fast-loading websites reduce bounce rates and improve user satisfaction.
- Search engine ranking factor: Page speed is a critical ranking factor for Google, and optimizing it through techniques like compression, caching, and using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) boosts SEO performance.
3. Mobile-friendliness
- Google’s mobile-first indexing: With mobile-first indexing, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites in search rankings. Technical SEO ensures your website is responsive and delivers a seamless experience across all devices.
4. Prevents duplicate content issues
- Consolidates ranking signals: Canonical tags and proper URL structures help consolidate traffic to the correct version of a page, preventing dilution of ranking power.
- Avoids penalties: Duplicate content can confuse search engines, leading to reduced visibility.
5. Boosts security with HTTPS
- Trust & Credibility: A secure site (HTTPS) is not only favored by search engines but also by users. It helps protect data and builds trust, encouraging visitors to engage with your site.
6. Optimizes site architecture
- Improved internal linking: A well-structured website makes it easier for crawlers to understand the hierarchy of pages, improving overall indexing.
- Efficient navigation: Clear navigation improves user experience, increasing the chances of conversions.
7. Reduces bounce rates

- Faster, error-free sites: Addressing technical issues like 404 errors, redirect chains, and server response times ensures users don’t encounter frustrations that lead them to leave.
8. Supports advanced SEO strategies
- Structured data & Rich snippets: Implementing schema markup enhances search result appearances with rich snippets, increasing click-through rates (CTR).
- Voice search optimization: Technical SEO plays a role in optimizing for emerging trends like voice search by emphasizing structured data and fast-loading content.
9. Future-proofing against algorithm updates
- Staying competitive: A technically optimized site is better equipped to handle algorithm changes that prioritize speed, mobile-friendliness, and user experience.
- Long-term benefits: Technical SEO lays the foundation for sustainable organic growth.
10. Provides actionable insights
- Data-driven improvements: Technical SEO audits highlight performance bottlenecks and areas for optimization, enabling targeted efforts to improve rankings.
How complicated is technical SEO?
Technical SEO can seem complex at first glance due to the variety of factors and tools involved. However, breaking it down into manageable components and following a systematic approach makes it less daunting.
Factors contributing to complexity
- Diverse skills required: Knowledge of web development, server configurations, and SEO principles is often needed.
- Constantly evolving guidelines: Search engines like Google regularly update their algorithms, requiring continuous learning and adaptation.
- Integration of multiple tools: Tools like Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs are essential but can be overwhelming for beginners.
Why is it manageable?
- Structured approach: Dividing tasks like crawlability, speed optimization, and mobile-friendliness into separate steps simplifies the process.
- Automated tools: Many tools provide automated insights and fixes, reducing manual effort. For example, plugins like Yoast SEO or RankMath streamline technical tasks for WordPress users.
- Resources & Communities: A wealth of tutorials, blogs, and forums (e.g., Moz, SEMrush, Google Webmasters) exist to guide and support you.
Tips to simplify technical SEO
- Start with an audit: Use tools like Screaming Frog or SEMrush Site Audit to identify and prioritize issues.
- Focus on fundamentals: Ensure your site is mobile-friendly, secure (HTTPS), and has a proper sitemap and robots.txt file.
- Learn gradually: Start with basics and progressively tackle advanced topics like structured data or Core Web Vitals.
When to seek expert help?
While small websites can often handle technical SEO in-house, larger, more complex websites may require professional expertise. Hiring an SEO expert ensures that intricate issues like international SEO, server-side configurations, or large-scale site migrations are handled effectively.
In summary: Technical SEO might seem challenging, but with the right tools, a structured approach, and continual learning, it’s entirely manageable. The key is to start with the basics and gradually build your expertise.
Key elements of technical SEO
1. Website architecture & crawling
The way your website is structured affects both user experience and search engine bots’ ability to navigate your site.
Importance of site architecture
A well-organized website structure ensures that both users and bots can easily find content. It directly impacts crawlability and link equity distribution.
Best practices for crawlability
A. Robots.txt file
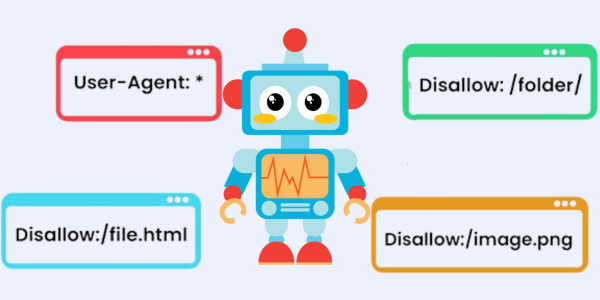
Create a robots.txt file to guide search engines on which parts of your site to crawl.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /private-data/
B. XML sitemap
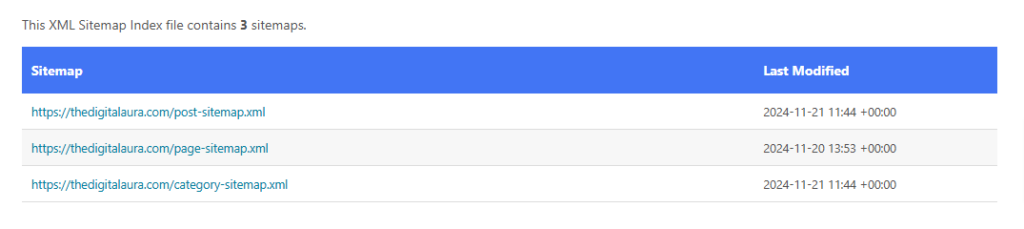
- Generate and submit an XML sitemap to search engines to provide a roadmap of your site.
Tools to use: Yoast SEO, Screaming Frog, or Google Search Console.
C. Resolve crawl errors
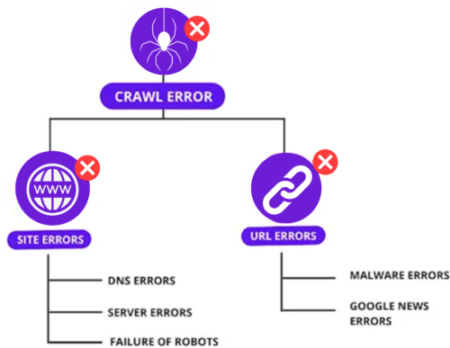
- Use Google Search Console to identify and fix 404 errors, broken links, or server issues.
2. Mobile-first indexing

Since Google transitioned to mobile-first indexing, your website’s mobile performance significantly impacts rankings.
Why does mobile optimization matter?
- Mobile devices account for over 60% of global website traffic.
- Google primarily uses the mobile version of your site for indexing.
Tips for mobile optimization
- Responsive web design: Ensure your site adapts to different screen sizes. Use CSS frameworks like Bootstrap.
- Optimize navigation: Use hamburger menus and clickable buttons for a smoother experience.
- Test mobile-friendliness: Tools: Google Mobile-Friendly Test, BrowserStack.
3. Page speed optimization
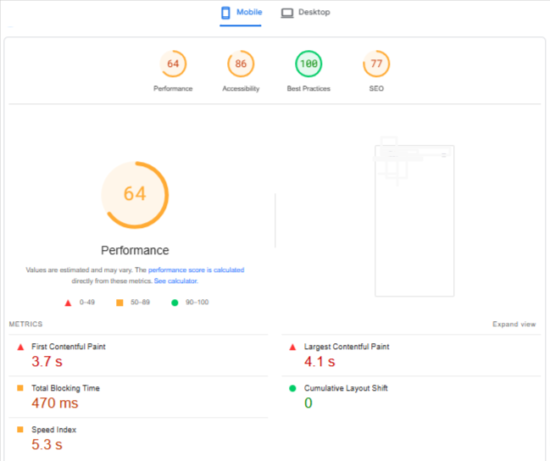
Page speed is a critical ranking factor and directly affects user engagement and bounce rates.
Analyzing page speed
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest to assess your site’s performance.
Strategies to improve speed
- Enable compression: Compress files using GZIP or server-side tools.
- Optimize images: Compress images with tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim. Use next-gen formats like WebP.
- Minify code: Remove unnecessary spaces and comments in CSS, JavaScript, and HTML. Use tools like UglifyJS or MinifyCode.
- Leverage browser caching: Configure caching in your .htaccess file.
- Use a CDN: Distribute content globally for faster delivery with services like Cloudflare or Amazon CloudFront.
4. HTTPS & Site security
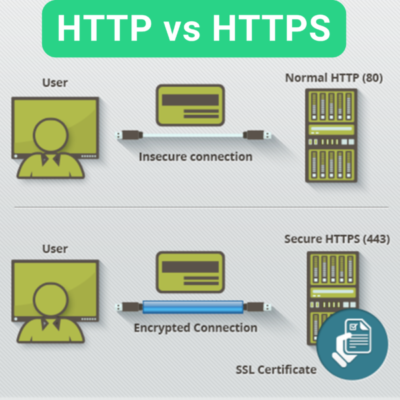
A secure website not only protects user data but also improves trustworthiness and rankings.
Implementing HTTPS
- Obtain an SSL certificate from providers like Let’s Encrypt or Comodo.
- Verify the HTTPS setup using tools like SSL Checker.
Regular security audits
- Update plugins and CMS platforms.
- Use tools like Sucuri Security or Wordfence for malware scanning and firewall protection.
5. Structured data & Schema markup
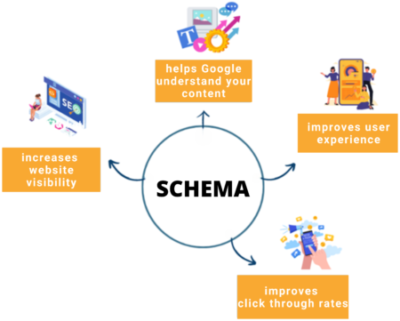
Schema markup enhances search engines’ understanding of your content and enables rich snippets, boosting CTR.
Types of schema markup
- Breadcrumbs: Help users navigate your site.
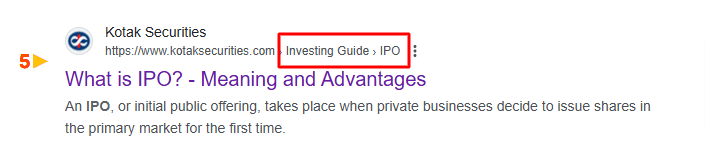
- Product schema: Display product prices, availability, and ratings.
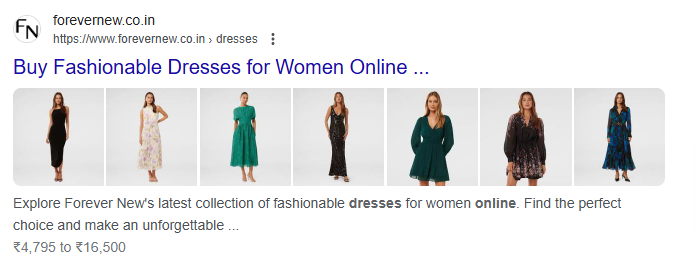
- FAQ schema: Ideal for blog content.
Tools for schema implementation
- Google structured data markup helper: For creating structured data.
- Yoast SEO plugin: Simplifies schema integration.
- Validate using Google’s Rich Results Test.
6. Core Web Vitals & User experience

Core Web Vitals are crucial metrics introduced by Google to assess page experience.
Key metrics
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Should occur within 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID): Should be less than 100 milliseconds.
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Aim for a score below 0.1.
How to improve Core Web Vitals?
- Optimize fonts by using font-display: swap.
- Lazy-load images using plugins or scripts.
- Minimize third-party scripts.
7. Duplicate content issues
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and lower rankings.
Common scenarios
- Printer-friendly pages.
- Session IDs in URLs.
Fixing duplicate content
- Use canonical tags to point to the primary version of the page.
- Implement 301 redirects for redundant pages.

8. International SEO
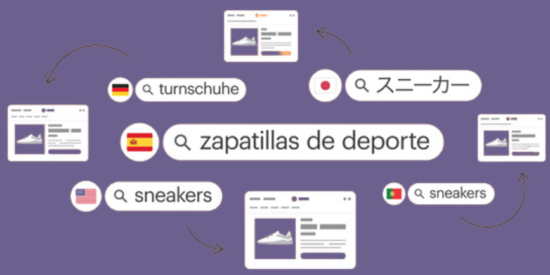
Catering to a global audience requires specific technical SEO practices.
Best practices
- Hreflang tags: Specify the language and region for pages.
- Localized content: Create region-specific pages.
- Use tools like Ahrefs to track international rankings.
9. Canonicalization

Canonicalization ensures search engines know which version of a page is the master copy, preventing duplicate content issues.
Why does canonicalization matter?
It helps avoid duplicate content penalties and consolidates ranking signals to the preferred page.
How to implement canonical tags?
- Add a <link rel=”canonical” href=”URL” /> tag in the <head> section of the preferred page.
- Use tools like Screaming Frog or Google Search Console to detect and fix issues.
10. URL structure optimization
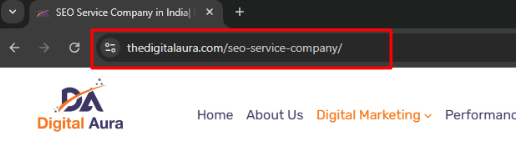
A clean and organized URL structure improves both user experience and crawlability.
Best practices for URL optimization
- Use short, descriptive URLs that include target keywords.
- Avoid dynamic parameters like ?id=12345.
- Maintain consistency with lowercase letters.
- Use hyphens (-) to separate words, not underscores (_).
Example
- Good URL: example.com/technical-seo-guide
- Bad URL: example.com/?p=12345
11. 404 error management

Handling 404 errors effectively ensures users and search engines don’t encounter dead ends.
Steps to manage 404 errors
- Regularly audit your site for broken links using tools like Ahrefs or Screaming Frog.
- Create a custom 404 page that helps users find relevant content.
- Redirect broken links to relevant pages using 301 redirects.
12. Pagination optimization
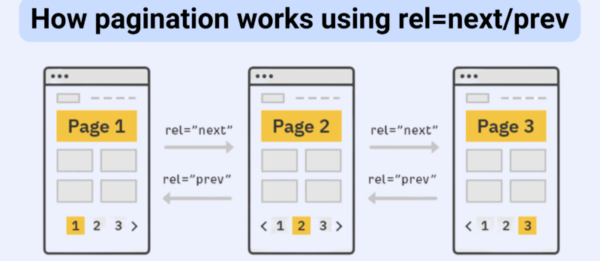
Pagination ensures large sets of content are split across multiple pages in a crawlable manner.
Best practices for pagination
- Use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” tags in the <head> section to guide crawlers.
- Include a canonical tag on paginated pages pointing to the main category page.
- Ensure each paginated page has unique meta descriptions and titles.
13. HTTP/2 implementation
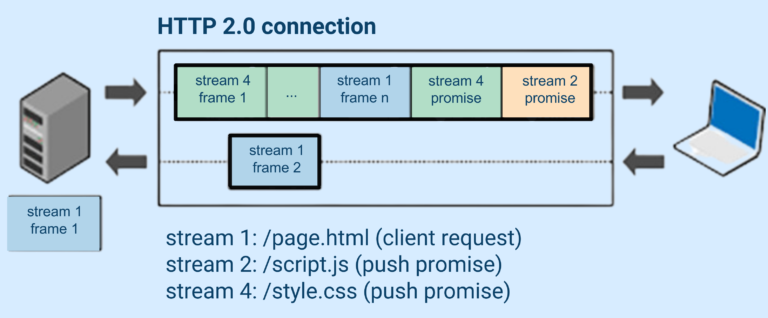
Upgrading to HTTP/2 can significantly enhance site speed and performance.
Why HTTP/2?
- Supports multiplexing: Multiple requests are handled simultaneously.
- Reduces latency, improving load times.
How to implement?
Check with your hosting provider if they support HTTP/2 and enable it through server settings.
14. Log file analysis
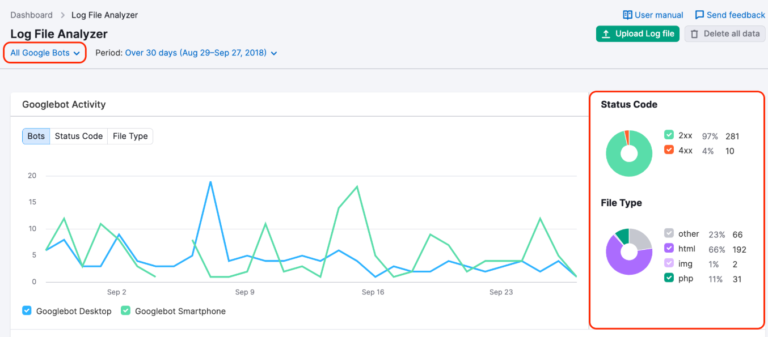
Log file analysis helps understand how search engines crawl your site.
Tools for log file analysis
- Screaming Frog Log File Analyzer.
- Splunk or ELK Stack.
Insights to gain
- Identify pages crawled most frequently.
- Detects crawl errors like 403 or 500 status codes.
- Analyze which bots (e.g., Googlebot, Bingbot) access your site.
15. Orphan pages
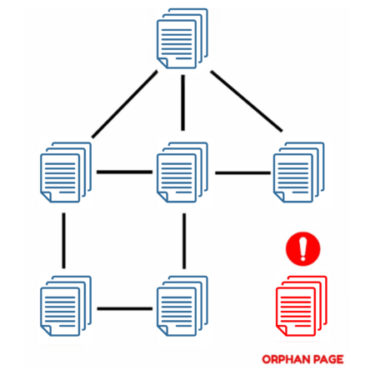
Orphan pages are those that aren’t linked from any other pages on your site, making them hard for search engines to find.
How to fix orphan pages?
- Use tools like Screaming Frog to identify orphan pages.
- Link these pages from relevant sections of your site.
- Include them in your XML sitemap.
16. Redirect chains & loops
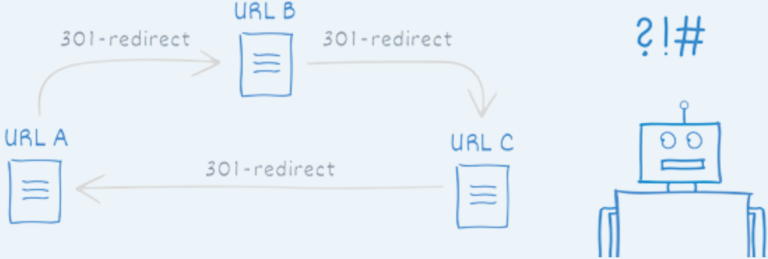
Excessive redirect chains or loops can confuse crawlers and slow down site performance.
How to fix it?
- Audit your site for redirect chains using tools like SEMrush.
- Replace chains with direct 301 redirects.
- Avoid creating infinite loops by testing redirects thoroughly.
17. JavaScript SEO
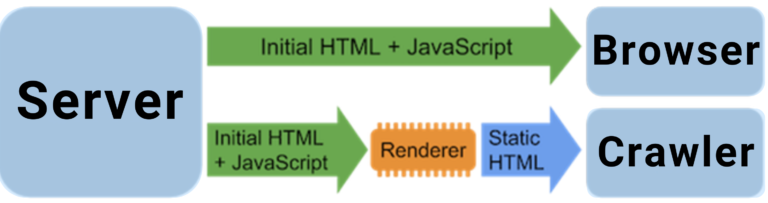
With more websites relying on JavaScript frameworks, ensuring your content is crawlable is vital.
Best practices for JavaScript SEO
- Use server-side rendering (SSR) or dynamic rendering.
- Verify what Googlebot sees using the “Inspect URL” tool in Google Search Console.
- Avoid hiding important content in JavaScript.
18. Multilingual SEO
If your site targets multiple languages or regions, multilingual SEO practices are crucial.
Key practices
- Use hreflang tags to specify language and regional targeting.
- Ensure translated versions are fully localized, including keywords and metadata.
- Avoid automated translations that reduce content quality.
19. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
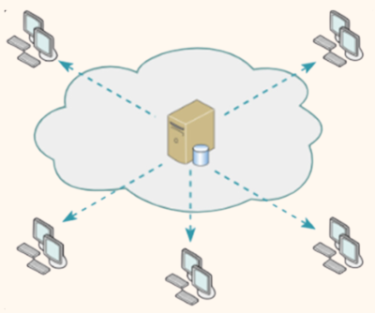
A CDN can dramatically improve loading times, especially for global audiences.
How to implement?
- Choose a CDN provider like Cloudflare, Akamai, or AWS CloudFront.
- Configure your website to serve static assets like images and scripts through the CDN.
20. Robots meta tags
Robots meta tags control how search engines crawl and index your pages.
Common robots meta tag values
- noindex: Prevents indexing of a page.
- nofollow: Prevents bots from following links on the page.
- noarchive: Prevents search engines from caching the page.
Usage example
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex, nofollow”>
21. Server response codes
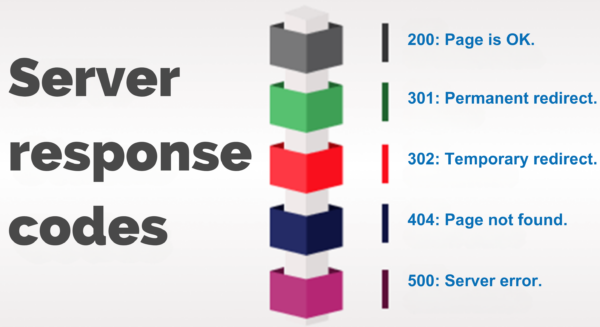
Proper server response codes help search engines understand the status of your pages.
Key codes to monitor
- 200: Page is OK.
- 301: Permanent redirect.
- 302: Temporary redirect.
- 404: Page not found.
- 500: Server error.
How to monitor?
Use tools like Screaming Frog or server logs to identify response code issues.
22. Image optimization for SEO

Images can boost your site’s visibility if optimized correctly.
Key steps
- Use descriptive file names and alt tags.
- Compress images with tools like TinyPNG.
- Serve images in next-gen formats like WebP.
Best technical SEO tools
Implementing technical SEO requires the right tools to analyze, monitor, and optimize your website’s performance. Here are some highly recommended tools to help you with technical SEO:
A. Crawling & Auditing tools
1. Screaming Frog SEO Spider
- Purpose: Comprehensive website crawl for SEO issues.
- Features: Identify broken links, missing metadata, duplicate content.
- Use: Ideal for auditing websites of any size to fix technical errors.
2. Sitebulb
- Purpose: SEO auditing with visual insights.
- Features: Crawl reports, structured data analysis, Core Web Vitals checks.
- Use: Best for visualizing complex site structures and audit findings.
3. DeepCrawl
- Purpose: Enterprise-level site audits.
- Features: JavaScript rendering analysis, crawl budget optimization.
- Use: Great for identifying indexing and crawlability issues on large sites.
4. Botify
- Purpose: Optimize enterprise websites for search engine crawling.
- Features: Log analysis, structured data insights, rendering optimization.
- Use: Suited for e-commerce or large, dynamic sites with complex architectures.
B. Page speed & Core Web Vitals
1. GTmetrix
- Purpose: Analyze and improve website loading speed.
- Features: Waterfall reports, Core Web Vitals metrics, video analysis.
- Use: Great for pinpointing bottlenecks in page performance.
2. Google PageSpeed Insights
- Purpose: Measure website performance on mobile and desktop.
- Features: Core Web Vitals insights, actionable suggestions for speed improvement.
- Use: Best for understanding Google’s perspective on page speed optimization.
3. Lighthouse
- Purpose: Assess website performance, accessibility, and SEO.
- Features: Detailed metrics for PWA compliance, performance scores.
- Use: Use for improving technical aspects directly affecting rankings.
4. WebPageTest
- Purpose: Advanced testing for performance bottlenecks.
- Features: Multiple device testing, real-world simulation, multistep transaction analysis.
- Use: Suitable for in-depth performance analysis and debugging.
C. Log file analysis tools
1. SEO Log File Analyzer by Screaming Frog
- Purpose: Monitor and analyze search engine bot behavior.
- Features: Visualize crawler activity, detect crawl errors.
- Use: Excellent for managing crawl budget and identifying indexation problems.
2. Splunk
- Purpose: Enterprise-level log analysis for technical SEO.
- Features: Log aggregation, crawl behavior visualization, advanced filtering.
- Use: Ideal for large websites needing detailed log insights.
D. Structured data & Schema validation
1. Google Rich Results Test
- Purpose: Validate structured data for eligibility in rich results.
- Features: Check markup for errors, preview search result appearance.
- Use: Essential for ensuring rich snippets display correctly in SERPs.
2. Schema Markup Generator (Merkle)
- Purpose: Create schema markup for various data types.
- Features: Simple interface, JSON-LD code generation.
- Use: Useful for quickly generating valid structured data.
3. SEO Structured Data Tool by Classy Schema
- Purpose: Validate structured data implementation.
- Features: Rich snippet testing, structured data optimization.
- Use: Ideal for fine-tuning schema for better SERP performance.
E. Mobile Optimization tools
1. Google Mobile-Friendly Test
- Purpose: Ensure mobile usability of web pages.
- Features: Detect mobile-specific issues, compatibility suggestions.
- Use: A must-use tool for maintaining mobile-first indexing standards.
2. BrowserStack
- Purpose: Test website compatibility across devices.
- Features: Real-time testing, debugging tools, and responsive design previews.
- Use: Great for ensuring consistent performance on various mobile devices.
F. Indexing & Sitemap tools
1. Google Search Console (GSC)
- Purpose: Monitor website indexing and search performance.
- Features: Sitemap submission, index coverage reports, performance metrics.
- Use: Core tool for tracking how Google indexes and ranks your site.
2. Bing Webmaster Tools
- Purpose: Optimize websites for Bing’s search engine.
- Features: Backlink data, keyword insights, and indexing tools.
- Use: Useful for tapping into Bing’s audience and refining strategies.
G. Security tools
1. SSL Labs
- Purpose: Test and validate SSL configurations.
- Features: Analyze SSL setup, detect vulnerabilities.
- Use: Essential for ensuring HTTPS compliance and secure user data.
2. Sucuri SiteCheck
- Purpose: Scan for malware and security risks.
- Features: Identify hacks, security gaps, and vulnerabilities.
- Use: Best for maintaining website safety and preventing blacklisting.
H. Content delivery & Caching
1. Cloudflare
- Purpose: Speed up website delivery through a CDN.
- Features: DDoS protection, caching, global content delivery.
- Use: Ideal for reducing latency and protecting against attacks.
2. Amazon CloudFront
- Purpose: Distribute content globally with low latency.
- Features: Edge caching, real-time metrics, and scalable delivery.
- Use: Suitable for high-traffic websites needing seamless performance.
Final thoughts
Technical SEO in 2025 is more crucial than ever. By following this comprehensive guide, you’ll ensure your website remains competitive, offering excellent performance, a seamless user experience, and top-notch security. Regular audits and updates are essential to maintaining your site’s health and maximizing its potential for higher rankings.
Start implementing these strategies today and dominate the search rankings in 2025!
Author Bio

Sejal Chopra
Sejal Chopra is a dedicated digital marketing executive at Digital Aura, specializing in SEO, content writing & performance marketing that drive measurable results. With a strong focus on data-driven campaigns, Sejal helps businesses optimize their online presence and achieve their marketing goals. She is skilled in leveraging various digital channels to enhance brand visibility and maximize ROI.
Sejal is passionate about staying on top of the latest trends in digital marketing and continually refining her approach to deliver impactful outcomes. Outside of work, she enjoys exploring new ideas and technologies to stay ahead in the dynamic marketing landscape.



